Graphical representation of the current state of information provides a
very effective means for presenting information to both users and
system developers.
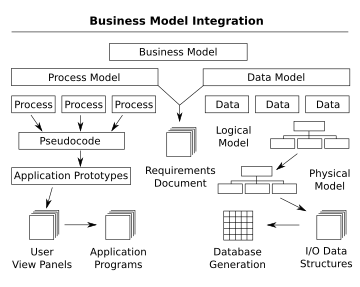
- A business model illustrates the functions associated with the business process being modeled and the organizations that perform these functions. By depicting activities and information flows, a foundation is created to visualize, define, understand, and validate the nature of a process.
- A data model provides the details of information to be stored, and is of primary use when the final product is the generation of computer software code for an application or the preparation of a functional specification to aid a computer software make-or-buy decision. See the figure on the right for an example of the interaction between business process and data models.
Usually, a model is created after conducting an interview, referred to
as business analysis. The interview consists of a facilitator asking a
series of questions designed to extract required information that
describes a process. The interviewer is called a facilitator to
emphasize that it is the participants who provide the information. The
facilitator should have some knowledge of the process of interest, but
this is not as important as having a structured methodology by which the
questions are asked of the process expert. The methodology is important
because usually a team of facilitators is collecting information across
the facility and the results of the information from all the
interviewers must fit together once completed.
The models are developed as defining either the current state of the
process, in which case the final product is called the "as-is" snapshot
model, or a collection of ideas of what the process should contain,
resulting in a "what-can-be" model. Generation of process and data
models can be used to determine if the existing processes and
information systems are sound and only need minor modifications or
enhancements, or if re-engineering is required as a corrective action.
The creation of business models is more than a way to view or automate
your information process. Analysis can be used to fundamentally reshape
the way your business or organization conducts its operations.
Computer-aided software engineering
Computer-aided software engineering (CASE), in the field software
engineering is the scientific application of a set of software tools and
methods to the development of software which results in high-quality,
defect-free, and maintainable software products. It also refers to
methods for the development of information systems together with
automated tools that can be used in the software development
process. The term "computer-aided software engineering" (CASE) can refer
to the software used for the automated development of systems software,
i.e., computer code. The CASE functions include analysis, design, and
programming. CASE tools automate methods for designing, documenting, and
producing structured computer code in the desired programming language.
Two key ideas of Computer-aided Software System Engineering (CASE) are:
- Foster computer assistance in software development and or software maintenance processes, and
- An engineering approach to software development and or maintenance.
Typical CASE tools exist for configuration management, data modeling, model transformation, refactoring, source code generation.
No comments:
Post a Comment